Getting Started with Kubernetes

With application development and deployment now critical to success in digital business, many organisations are turning to containers, as a lighter weight alternative to the Virtual Machine or VM. By sharing the same underlying host operating system, containers have the edge over VMs, in terms of their resource consumption. However, managing containers can pose complex challenges -- which is where Kubernetes comes into the picture.
What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is an orchestration tool for containers. In essence, it is an open-source container orchestration engine for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerised applications. The name derives from Ancient Greek, and is a root for modern English language terms like “governor” and “gubernatorial”.
In its governorship role, Kubernetes helps to ensure that containerised applications run where and when you want them to. It also assists the applications in finding the resources and tools they need to work.
Benefits of Using Kubernetes
Kubernetes can speed up the development process by making easy, automated deployments and updates. In addition to managing apps and services with almost zero downtime Kubernetes also provides self-healing. The engine has the ability to detect and restart services when a process crashes inside the container. For the organisation, Kubernetes greatly simplifies deployments and makes sure that workloads are fully utilised – thereby lowering costs, and increasing operational velocity.

Kubernetes functionality extends to the following areas:
- Load balancing
- Horizontal scaling (scaling out) to accommodate fluctuating workload demands
- Secrets and configuration management
- Self-healing infrastructure
- Storage management
This combination provides a number of benefits to the organisation, as summarised in the infographic below:

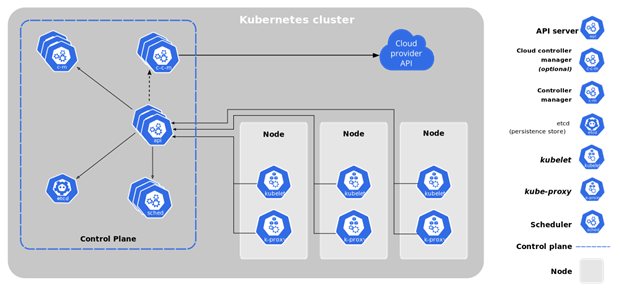
Kubernetes Components
[Image source: Kubernetes.io]
There are a number of key elements that make up the Kubernetes architecture. These components include:
Master Node
This is the main point of entry for all administrative tasks, which is responsible for orchestrating the worker nodes.
Worker Node
Formerly referred to as minions, worker nodes carry out specified tasks, as laid down by the Master Node.
Node
Nodes are responsible for running containers inside pods. When using container technologies such as Docker and rkt, the node provides the enabling environment for downloading images and starting containers.
Primary Node Agent
This is the Kubernetes component responsible for ensuring that containers are running, and in a healthy condition.
Pod
In Kubernetes, a pod is a deployment instance which is capable of hosting multiple containers and storage volumes. Each pod has a unique IP Address within the Kubernetes cluster, and containers within the same pod have access to shared volumes.
Deployment
A deployment provides a blueprint for the creation of pods, based on a specifications template. The deployment is responsible for running and updating the pods in a controlled manner. Note that one deployment can have multiple pods, and is capable of scaling up replicas of the pods within its domain.
Secret
A secret is a Kubernetes object that can store sensitive information like passwords. It’s possible to specify an encryption configuration (EncryptionConfig) to apply secure encryption to a secret.
Service
Within Kubernetes, services can provide a number of functions. A ClusterIP service can make a deployment visible inside the cluster, and load balance traffic between the pods of the deployment. A Node Port service can bind a deployment to a port of the Master Node. A Load Balancer service can assign a public IP address to a deployment, exposing it to the internet.
Kubelet
Responsible for the functioning of the container execution layer, Kubelet is a critical service within Kubernetes that can decouple the management of individual applications from each other, and from management of the underlying cluster’s physical or virtual infrastructure.
API Server
This acts as the communications medium for all the components in the cluster, and exposes the Kubernetes API (Application Programming Interface).
Scheduler
The scheduler is responsible for assigning applications or Kubernetes objects to a worker node. It places pods on the nodes, based on their resource requirements.
Getting Started
To gain experience of using Kubernetes and mastering its features, there are several avenues you can follow. They include:
Minikube
If you’d like to experiment with a single-node Kubernetes cluster in a virtual machine on your personal computer or laptop, Minikube is a beginner’s level tool. It generates a single node which is also a master, providing the experience of working with a node -- but not the multiple nodes typical of a working Kubernetes deployment.
Katacoda
This is an interactive browser-based tool. Once you sign into the service, you can run Kubernetes scenarios directly in the Katacoda terminal.
Google Kubernetes Engine
The Google Kubernetes Engine lets you create a free tier account. Once you sign in, you can use the Google infrastructure to deploy, manage, and scale containerised applications in a managed, multi-node cluster environment.
Microsoft Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
As with Google, you can create a free tier account to get up and running immediately with an Azure environment that offers serverless Kubernetes, an integrated continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) experience, plus enterprise-grade security and governance.
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS)
Rounding out the Kubernetes offerings of the major cloud providers, Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service also offers a free tier account with AWS for the deployment, management, and scaling of containerised applications.
Kubernetes Dashboard
This dedicated tool is a web-based User Interface that enables you to deploy containerised applications into a Kubernetes cluster, and perform troubleshooting and resource management tasks within the cluster. Note that to deploy the Kubernetes Dashboard, you require a working instance of the kubectl CLI Command Line Interface.
Partnering for Kubernetes Success
Established in 2002, zsah provides managed cloud, DevOps, D&A, and IT services. Our technical and service delivery capabilities span the tech sector from simple, secure cloud hosting to data analytics, software development and beyond, to add value to your existing functions or complement your IT operations, where and when you want.
We offer fully managed Kubernetes hosting, hybrid cloud management, and migration services. With zsah's Kubernetes services, we take care of all the hassle of maintaining and managing your Kubernetes infrastructure.
Our team of experts ensure you have the optimum solution for your needs, whether you're a startup planning for future growth, or an enterprise who needs a mature Hybrid Cloud Strategy. For larger applications, we devise an optimal, fully managed, multi-cluster Kubernetes hosting architecture based on your needs. If your organisation favours a hybrid cloud Strategy, we can also manage Kubernetes clusters across all the major clouds and on-premises.
Our team will develop optimal environments to host your applications in the cloud. In addition, zsah offers 24/7/365 application support and investigatory skills in application performance and error fixing.
If you would like to learn more about how zsah can help you get started with Kubernets, get in touch with us.