Mastering Cloud Best Practices: Balancing Security, Efficiency, and Sustainability

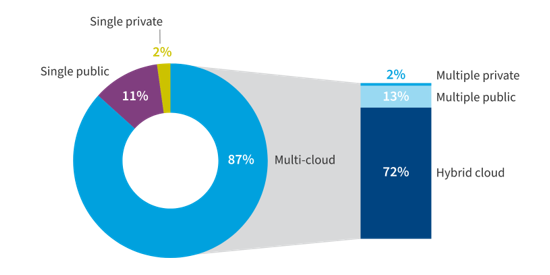
More and more businesses continue to move away from traditional data centres and embrace the power of cloud computing. Indeed, according to the Flexera State of the Cloud Report 2023, 87% of organisations now embrace multi-cloud environments.
(Image source: info.flexera.com
This uptake means it is essential that organisations understand and implement cloud best practices.
Below, we explore various aspects of cloud computing, from disaster recovery and security to leveraging the right cloud services for your application. We also discuss the importance of green cloud computing and its impact on your business and the environment.
We begin with two critical components for a robust disaster recovery plan – RPO and RTO.
RPO/RTO – Definitions and Implementation
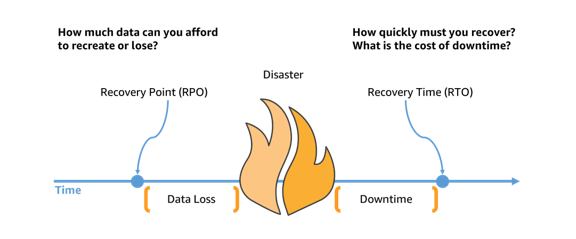
Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO) are both crucial factors in a comprehensive DR plan. RPO refers to the maximum amount of data that can be lost during an incident without causing significant harm to the business, while RTO is the maximum acceptable time to recover from an incident and resume operations.
(Image source: aws.amazon.com)
To define RPO and RTO for your business, begin by evaluating the criticality of various applications and data. Identify which data is indispensable and which can be restored after a longer delay. Conduct a thorough risk assessment to determine the potential impact of data loss or downtime on your organisation.
Once you have established your RPO and RTO, integrate these metrics into your disaster recovery plan. This will ensure that your business can recover quickly from unexpected events, minimising disruptions, and financial losses.
Restore/DR Test Recovery: Testing Frequency and Documentation
Regularly testing your disaster recovery plan is crucial for ensuring that it functions as intended. Conduct restore and DR tests at least once a year or after significant changes to your infrastructure or applications. However, more frequent testing is recommended for critical systems or when required by regulatory bodies.
During a test, simulate various disaster scenarios and document the recovery process, identifying any gaps or shortcomings. Review and update your recovery plan based on the results and share the findings with relevant stakeholders.
Data Storage Regulations and Sovereign Cloud Compliance
As data privacy and security regulations continue to evolve, businesses must ensure their cloud storage practices are compliant. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other regional regulations govern data storage and handling, affecting organisations worldwide.
One solution is to utilise sovereign cloud services, which store data exclusively within a specific country or jurisdiction. This approach can help your business maintain compliance with local regulations while enjoying the benefits of cloud computing.
Ensure that your chosen cloud service provider complies with the relevant data storage regulations and that they can demonstrate their commitment to data security through certifications and audits.
IAM Solutions: The Cornerstone of Cloud Security
Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions form the backbone of cloud security, ensuring only authorised individuals can access specific resources. A robust IAM system incorporates components like multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and user behaviour analytics. By using such a system, you can manage identities, credentials, and access rights effectively, thereby protecting your data and applications from unauthorised access. In addition, IAM solutions enable you to track user activities, providing valuable insights for audit purposes and helping detect potential threats.
To leverage IAM solutions effectively, choose a solution that aligns with your business needs and integrates seamlessly with your existing IT infrastructure.
SASE: The Future of Network and Security
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) is a network architecture model that combines network security and wide area networking capabilities in a single cloud service. SASE eliminates the need for multiple standalone security tools by offering a comprehensive suite of security services, including secure web gateways, firewall-as-a-service, and zero trust network access. As more businesses adopt remote work and cloud-first strategies, the importance of SASE architecture grows. Implementing SASE can reduce network complexity, improve performance, and enhance security.
However, it is essential to partner with a SASE provider that can meet your organisation's specific needs and provide continuous support during your SASE journey.
Encrypting Data: Safeguarding Your Cloud Assets
Encrypting your data is a non-negotiable aspect of cloud security best practices. It involves converting your data into a format that only authorised parties can decipher, providing a critical layer of protection for your sensitive information, whether at rest or in transit. Strong encryption algorithms and good data security practices are essential for effective data encryption. Furthermore, some regulatory bodies require specific types of encryptions. For example, the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) codified data encryption as a crucial aspect of data privacy. In the US, there are hundreds of laws enacted on both the federal and state levels that serve to protect the personal data of US residents. Most countries around the world also have their own data privacy laws that require encryption as a vital facet of data protection. As such, you will need to familiarise yourself with the legal requirements in your areas of operation.
It is also important to note that while cloud providers often offer encryption services, the responsibility to ensure that your data is adequately protected legally remains yours.
Penetration testing and Vulnerability Testing: Proactive Cloud Security Measures
Penetration testing (or pentesting for short) and vulnerability testing are proactive measures to detect and address potential weaknesses in your cloud environment. Pentesting simulates cyberattacks to identify exploitable vulnerabilities in your system. Vulnerability testing, on the other hand, is a systematic examination of your cloud environment for security weaknesses.
Regular pentesting and vulnerability testing can uncover hidden threats, help you understand your cloud security posture, and guide you in prioritising security improvements. However, these tests should be conducted by certified professionals to ensure accuracy and prevent unintentional damage.
Leveraging the Right Cloud Services for Your Applications
Selecting the appropriate cloud services for your applications is essential for optimising performance, security, and cost-efficiency. Evaluate your applications' specific requirements, considering factors such as processing power, storage capacity, and latency.
Consider using a combination of Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) to meet your business needs. Hybrid and multi-cloud strategies can provide additional flexibility, allowing you to take advantage of the best offerings from multiple providers.
Green Cloud: Embracing Sustainable Cloud Computing
The environmental impact of cloud computing is becoming increasingly important as businesses strive to reduce their carbon footprint. Opt for cloud service providers that prioritise sustainability, utilising renewable energy sources and adopting energy-efficient practices.
Assess your current cloud usage and identify areas where you can reduce energy consumption and waste. Implementing green cloud best practices, such as resource optimisation and server consolidation, can help you minimise your environmental impact while maintaining performance and cost-efficiency.
Building the Right Team: In-house, Outsourcing, or a Combination?
When it comes to managing cloud operations, businesses have several options: building an in-house team, outsourcing to a third party, or a combination of both.
To determine the best approach for your organisation, consider the following factors:
- Skill set: Assess the existing skill set of your team and identify any gaps. If you have a strong in-house team with cloud expertise, you may only need minimal external support. However, if your team lacks the necessary skills, you may need to invest in training or hire new talent.
- Cost: Analyse the costs associated with each option, including hiring, training, and retaining staff. To put this in perspective, the average cost to hire a cloud security specialist in the UK is £74,098 per year and this does not include employee benefits and other perks. Outsourcing can, therefore, be a more cost-effective solution for some businesses, especially those that need access to specialised expertise and have limited hiring budgets.
- Flexibility: Outsourcing can provide greater flexibility, allowing your organisation to scale up or down as needed. However, an in-house team may offer better control over your cloud operations.
- Security and compliance: If your business operates in a highly regulated industry or handles sensitive data, consider the security implications of each option. An in-house team may offer greater control over data security, while outsourcing may expose you to additional risks.
Ultimately, the right approach for your business will depend on your unique requirements and goals.
Finally, adopting cloud best practices is crucial for businesses looking to leverage the benefits of cloud computing while managing risks and maintaining security. By understanding and implementing RPO and RTO, conducting regular recovery testing, ensuring data storage compliance, selecting the right cloud services, and embracing green cloud computing, your business can stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of cloud technology. For help migrating and managing your cloud operations, contact zsah for managed cloud services. Our team of experts can provide guidance and assistance with the entire process.
eBook - Guide to Managed Cloud Services for Saas Providers
All the knowhow to help you implement a successful managed Cloud Strategy.