Private Cloud Hosting: Ultimate Guide For SaaS Businesses

Large or small, all SaaS companies will eventually have an important business decision to make – where to host their application? And the main choices usually come down to Public or Private Cloud Hosting.
Today, more and more SaaS companies are considering cloud-based solutions for their hosting needs – but not all cloud hosting solutions are created equal.
While the most common form of cloud hosting is public cloud, private cloud hosting offers a certain range of benefits – including improved security, increased flexibility, and the highest degree of visibility.
These private networks offer more security than public clouds because they provide complete isolation from outside threats. Additionally, private clouds offer better performance through higher bandwidth connection speeds with lower latency times for accessing data in remote locations. This makes it perfect for high-bandwidth workloads – which can often be vital to many SaaS providers.
In addition, private clouds also have cost benefits. Shifting data and computing workloads of your SaaS app from a public cloud to a private one can lead to significant savings. Perhaps the best example of this is Dropbox. The company started off on Amazon Web Services (AWS) but later moved its operations into a private cloud - rented off-premise data centers - retaining about 10% at AWS (a hybrid arrangement). The result was savings of $74.6 million in recurrent operational expenses.
So – what is private cloud hosting, what are the specific advantages of going private, and what kind of businesses stand to gain the most benefit?
Below, we explore the answers to these questions in order to help you make the best hosting decision for your business.
Private Cloud Hosting
The key differentiator that sets private cloud hosting apart from its public cloud counterpart is that private cloud delivers a cloud infrastructure set up specifically and exclusively for one single organisation.
When a SaaS company hosts their application in a public cloud, such as AWS (Amazon Web Services) or Microsoft Azure, cloud resources like servers and storage are owned and operated by the cloud service provider and delivered over the internet.
In a public cloud scenario, the business shares the same hardware, storage and network devices with other businesses that have subscribed to the same service.
Private cloud hosting, however, provides a distinct and secure cloud-based environment that consists of computing resources accessible only to one organisation.
In a private cloud, the infrastructure and services are managed and maintained on a private network, with both the hardware and software dedicated solely to one business only.
This provides greater control and privacy, and having dedicated resources ensures that there are no “noisy neighbours” (as there can be in a public cloud) to compete with for storage, processing and bandwidth.
Private Cloud Can Exist Either On- or Off-Premises
There are two primary types of private cloud – on-premises and off-premises. Also called an internal cloud, an on-premises private cloud is hosted within an organisation’s own offices or data centre.
The major benefit of an on-premises solution is that it offers organisations complete control and flexibility of their entire cloud infrastructure.
However, the downside is that it also means that the organisation will have to carry the full burden of hardware costs, software licensing and maintenance.
As such, many organisations choose an off-premises private cloud that is managed and maintained by a cloud provider such as zsah.
Off-premises private clouds are more cost-effective than internal clouds, and don’t require the business to maintain critical redundant systems such as infrastructure, power, cooling, networking and storage with a full-time in-house IT team.
Essentially, the key difference with off-premises private clouds is that the physical resources are located in a third-party facility owned by a cloud services provider.
As with an on-premises private cloud, the resources remain dedicated to – and managed and operated by – a single organisation, and not shared with other businesses, even if there are other businesses’ off-premises private cloud setups being operated in the same third-party facility.
Today, public cloud providers are now offering off-premises private cloud solutions with virtual private clouds (VPCs).
In effect, VPCs are private clouds that exist within a public cloud. Providers, such as Amazon VPC, isolate a specific portion of their public cloud infrastructure for one organisation’s private use.
Though the server setup resides within the public cloud, its resources are not shared with any other business than the specified VPC customer.
In a virtual private cloud model, the public cloud provider is responsible for ensuring that each VPC customer’s data remains isolated from all others.
The infrastructure is managed by the public cloud vendor, and the VPC customer retains control over the virtual networking environment, which can be configured according to the business’s precise needs with all resources accessed remotely.
Businesses can employ a managed technology services provider like zsah, who specialise in the configuration and management of VPCs, to manage and maintain their virtual private cloud environment.
VPCs are often considered to deliver the best of both worlds – organisations get a private cloud for added security and performance, and enjoy the reduced infrastructure costs that come with public clouds.
Off-premises private cloud is a growing market.
Research last year from the International Data Corporation (IDC) forecasts that spending on off-premises cloud IT infrastructure will grow at a five-year compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.8%, reaching $55.7 billion in 2022.
The report notes that, combined with on-premises private cloud, overall spending on private cloud IT infrastructure will grow at a 10.9% CAGR, and will surpass spending on non-cloud IT infrastructure by 2022, which will decline at a 2.7% CAGR during the same period.
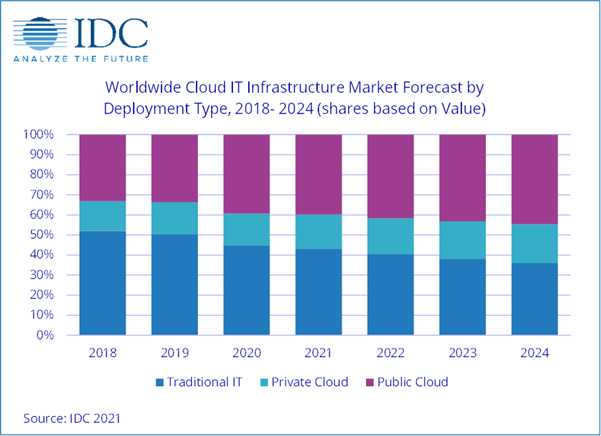
(Image source: idc.com)
The Advantages of Private Cloud Hosting
So, why are organisations attracted to going private?
Well, there are a number of advantages of private cloud hosting, chief among them being heightened levels of security.
Opting for an on-premises solution offers the highest levels in this regard, though utilising a provider for an organisation’s private cloud hosting needs will still provide greater control and security than what’s available with a public cloud solution.
Since resources are not shared with anyone else in a private cloud, with access absolutely restricted to the specified organisation only, an incredibly secure private network is created.
Other benefits include enhanced customisation options and greater control over the cloud environment.
With private cloud, organisations can customise their cloud environment to meet specific business and IT requirements.
Again, being the only user of the server setup means that organisations are able to configure and manage it in line with their precise needs – including any software and the operating system – and achieve a finely-tuned and highly-tailored network solution.
Private cloud hosting networks also benefit from being extremely reliable, scalable, and cost-effective – particularly with off-premises private cloud, which allow organisations to expand their data centre capacity without incurring massive capital expenditures on new hardware, which then have to be managed and maintained in-house.
What Types of Businesses Should Choose Private Cloud Hosting?
For companies with considerable performance, security and privacy concerns, private cloud hosting can be the ideal solution to manage them.
Though organisations typically incur higher costs in terms of time, money and resources to implement and manage a private cloud, they benefit from greater flexibility, enhanced customisation capabilities, higher security and better performance than public cloud solutions.
In addition, if they team up with the right provider, they gain a trusted technology partner also.
Any sites that deal with private customer data will benefit from private cloud hosting, as maximum security surrounding information assets can be assured.
FinTech and SaaS companies operating in the financial services sector, for example, handle extremely sensitive customer information, which would be exposed to heightened security risks in the public cloud.
Similarly, government agencies, large financial institutions, cybersecurity companies, and many other mid- to large-size organisations with business-critical operations and large or resource-heavy applications are all also ideally suited to a private cloud hosting solution.
Ultimately, the primary benefit of private cloud hosting is that it offers the highest level of control and security.
As such, SMEs with small-scale operations and tighter cost restrictions will likely be better off utilising a public cloud for their SaaS hosting needs, whereas high-level businesses that require a scalable, reliable, flexible and secure hosting solution stand to benefit greatly from private cloud hosting.
zsah Managed Technology Services
The benefits of private cloud hosting are maximised when organisations leverage the resources and skills of a reputed and reliable cloud provider like zsah.
Get in touch with us today to find out more about our private cloud hosting solutions, and how we can work with you to create a custom private cloud or virtual private cloud that is perfect for your business, and ensures your SaaS applications are safe, fast, secure, private and compliant.

